Flexible Precision: How Smart Materials Are Shaping the Future of Medical Equipment

Besides high-tech imaging and robotic surgery, there are many other modern innovations in healthcare. Sometimes, it’s the smallest, most flexible components—like endoscope bending rubber—that play a pivotal role in advancing medical equipment. These items form the basis for the right functioning, safety and accuracy of medical devices used uniformly around the world.
This article explores the fascinating science behind endoscope bending rubber and its transformative impact on medical technology.
Understanding Endoscope Bending Rubber:
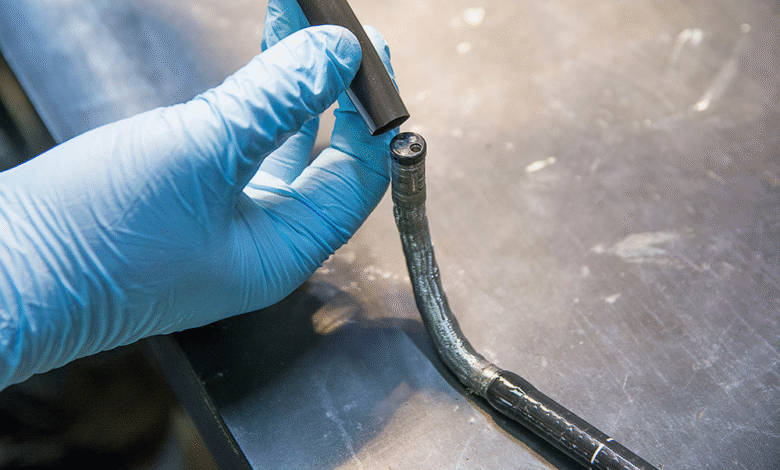
At first glance, the term “endoscope bending rubber” might seem technical and obscure, but it represents a critical component that enables endoscopes to navigate the complex pathways of the human body with agility and control. A doctor can use an endoscope to inspect the inside of your body because it has cameras, lights and is long and flexible. It is in the bending area that an endoscope bends and moves exactly where required, with help from the flexible rubber layer wrapping it.
The flexible rubber makes the tip of the endoscope angle and bend easily under control. It makes it possible for physicians to gently navigate the tool through difficult areas including the gastrointestinal tract, respiratory system or urinary tract. Lacking this piece, the rigid body of an endoscope would make it difficult for the doctor to move and see the area which would not only be uncomfortable for the patient but could also give wrong results.
The unique mechanical properties of endoscope bending rubber allow it to absorb stresses and maintain elasticity under repetitive motion. This gives room to bend the device which keeps its sensitive parts, like fiber optics and wires, safe. Basically, the rubber has to show both strength and flexibility to succeed in minor surgical procedures.
Role of Bending Rubber in High-Performance Medical Equipment:
There is much more to rubber bending than having a flexible substance. In high-performance medical equipment, it is integral to ensuring safety, precision, and longevity. Both skill and accuracy are required in endoscopic procedures and these two qualities depend a lot on the properties of the bending section of the tube.
Since endoscopes are used in tight spaces, the flexible part must bend as expected when the physician turns it. How fast patient feedback is dealt with can influence the outcome of the procedure. In gastrointestinal endoscopy, fine adjustment of the endoscope can determine if you spot a minor lesion or not. So, the curved rubber helps ensure the accuracy of diagnosis and the effectiveness of treatments.
Bending rubber should survive exposure to the strong chemicals used in sterilization. Instruments are regularly subjected to hot temperatures, different chemicals and mechanical strain to guarantee there are no contaminants. Staying safe and protecting a device requires bendable rubber with good chemical resistance and the right durability.
As well, in cases where precise control is very important, like in robotic-assisted surgery, flexible rubber parts are made to move smoothly and not sacrifice their strength. Because they play a key part in advanced medical systems, materials science shows how small improvements at this level can provide better care for patients.
Material Innovation in Endoscope Bending Rubber:
Innovation in materials science continues to revolutionize the design and performance of endoscope bending rubber. Usually, silicone rubber is what is used because it is easy for the body to accept, flexible and resistant to high temperatures. Because of continued research, new products and mixtures are being added that raise the limits of what bending rubbers are able to do.
Today, formulations offer greater protection against wear and increased flexibility, so batteries work for much longer and with greater stress. Some companies are blending materials such as silicone, polyurethane or fluorinated elastomers to create rubber that is both soft and tough. They provide top mechanical support with the comfort required for patients.
The inclusion of nanoparticles due to nanotechnology is making materials both tougher and stronger when it comes to abrasion, heat and chemical breakdown. These developments not only extend the service life of medical equipment but also reduce maintenance costs and downtime, which are critical considerations in busy healthcare settings.
Material inventors are becoming more interested in sustainability. Biodegradable or recyclable elastomers are being investigated in medicine which could reduce the negative impact on the environment without affecting how effective these materials are. The environmentally friendly approach agrees with worldwide trends in making healthcare greener.
Quality Standards in Manufacturing:
Given its crucial role, the manufacturing of endoscope bending rubber adheres to stringent quality standards. The FDA and ISO establish exacting guidelines so that these components meet safety and performance criteria.
Precise machinery is used by manufacturers to make rubber sections that are smooth and even in all places. Changes in small amounts can make the product less flexible and less resilient which could harm the entire device.
Ensuring quality means that testing is carried out mechanically for tensile strength, elasticity and cyclic bending. It is checked through chemical analysis that the material will not be damaged by common sterilization solutions. Biocompatibility tests verify that the rubber is safe when it interacts with the body’s tissue.
Manufacturers also set up advanced tracking systems to watch over how well batches are produced and to be able to trace them if necessary. This approach ensures accountability and rapid response in the event of any issues, reinforcing the reliability of medical equipment.
What the Market Needs and Where the Technology Might Go?
The demand for advanced medical equipment featuring durable and flexible components like endoscope bending rubber is rising sharply. Because of the increasing number of minimally invasive procedures, high-quality and dependable endoscopes are needed more often.
Asia, Latin America and the Middle East are growing the global economy through the rise of new healthcare facilities and the spread of health knowledge. At the same time, developments in telemedicine and remote surgery lead manufacturers to design parts that make operating small objects much simpler.
Bending rubber has many possible uses in medical devices in the future. Like endoscopes, other similar materials are used for catheters, flexible surgical equipment and health monitors people can wear. Bending rubbers that react quickly to changes in temperature or pressure using smart materials could soon have adaptive features that help improve their function in real time.
Teamwork among material scientists, engineers and healthcare professionals promises many interesting advances. With their research, they are expanding the possibilities for medical devices to become more adaptable, tough and sensitive which will positively impact international healthcare.
Conclusion:
The unassuming endoscope bending rubber is a testament to the power of smart materials in transforming medical equipment. Doctors depend on its flexibility, durability and compatibility with living tissue for minimally invasive methods in diagnostics and treatment.
Because quality standards keep improving and new materials are emerging, bending rubber will always be important in the field of medical device engineering. Simplex’s changing role improves and secures the technologies of today and opens doors to new innovations.
Awareness of these key factors explains the advanced science involved in medical improvement, pointing out that everyday items can make a big difference to healthcare.