What is Energy Storage PCS?
During the profound transformation of the global energy structure, clean energy sources like photovoltaics and wind power are developing at an unprecedented pace. However, these “weather-dependent” energy sources (often called variable renewables) are intermittent and variable. Their large-scale integration poses a severe challenge to the stable operation of the power grid. Energy Storage Systems (ESS), akin to a giant “power bank” for the grid, enable the “time travel” and “flexible dispatch” of electrical energy, becoming the key to solving this problem. Within an ESS, the Power Conversion System (PCS) is the core hub connecting the battery (DC side) to the grid or load (AC side), shouldering the critical responsibilities of bidirectional energy conversion, intelligent system control, and active grid support.
1. What is an Energy Storage PCS?
An energy storage PCS, whose full Chinese name is ‘储能变流器’ (meaning ‘energy storage converter’), is an intelligent power electronic device capable of bidirectional conversion between direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC). Think of it as an efficient, intelligent “bilingual translator” and “traffic commander”:
- When renewable generation is abundant or during off-peak hours, creating a grid power surplus, the PCS acts as a “rectifier,” converting the grid’s AC into DC to charge the battery bank, storing the energy.
- During peak demand, when electricity prices are high, or when the grid requires support, the PCS acts as an “inverter,” converting the DC stored in the batteries into clean AC, feeding it back to the grid or supplying local loads.
Beyond its core “translation” function, the PCS also integrates numerous features such as power quality optimization, system protection, and grid-connected/off-grid switching, making it the combined “brain” and “heart” of the energy storage system.
2. Main Functions of an Energy Storage PCS
- 2.1 Bidirectional Power Conversion: The Core Function
This is the most fundamental and core function of the PCS, ensuring the free flow of energy in both directions.- AC → DC (Rectification/Charging Mode): Draws power from the grid to charge the batteries.
- DC → AC (Inversion/Discharging Mode): Releases energy from the batteries, feeding it back to the grid or loads.
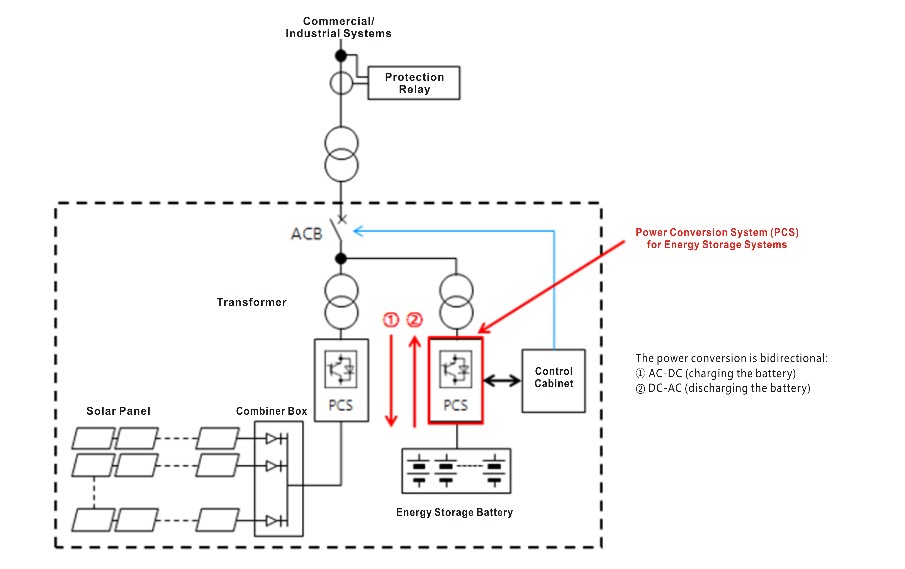
- 2.2 Power Quality and Grid Support: The Grid’s “Stabilizer”
The PCS possesses precise voltage and frequency control capabilities, enabling it to:- Maintain stable and pure output voltage, reduce harmonic pollution, and improve power supply quality.
- Quickly inject reactive power when grid anomalies such as momentary voltage sags or frequency fluctuations occur, supporting grid voltage and frequency recovery to prevent cascading failures (avalanche-type blackouts).
- Support Low Voltage Ride-Through (LVRT) and Fault Ride-Through (FRT), ensuring that during brief grid faults, the energy storage system not only remains connected but also actively helps restore normal grid operation. This makes it a grid-forming or grid-supporting asset.
- Energy Management and Dispatch Response: The Clever “Economist”
By interfacing with the upper-level Energy Management System (EMS), the PCS can intelligently decide when to charge and discharge based on preset strategies.- Considered factors: Real-time electricity prices, grid load conditions, renewable energy generation forecasts, and user consumption habits.
- Value realization: Peak shaving and valley filling (charging when prices are low, discharging when prices are high), demand response (complying with grid dispatch instructions), and load following, thereby creating economic benefits for users.
- Fluctuation Smoothing and Output Stabilization: The “Buffer” for Renewable Generation
To address the issue of fluctuating output from PV and wind power, the PCS can control the rapid charging and discharging of the storage batteries, smoothing their power fluctuations. This results in a stable, controllable output curve, significantly reducing the impact on the grid.
3. Key Technologies of Energy Storage PCS
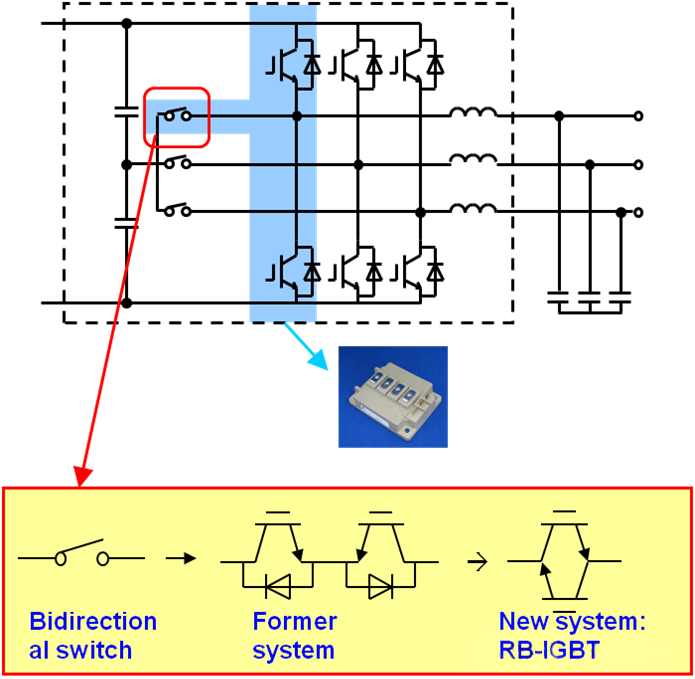
- Three-Level Inverter Technology: A Superior “Waveform Sculptor”
Traditional two-level inverters produce waveforms resembling steep staircases, with high harmonics and losses. Three-level inverter technology can output positive, zero, and negative voltage levels, resulting in a waveform closer to a smooth sine wave.
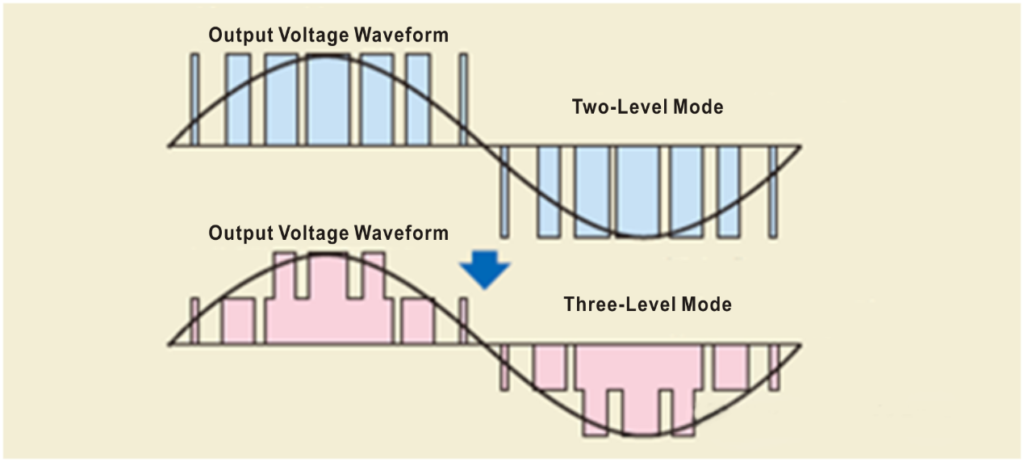
- Advantages: Lower harmonic content and superior power quality; lower switching losses and higher overall efficiency (typically >98.5%); lower voltage withstand requirements for components, leading to higher system reliability.
- Currently, three-level topologies based on new-generation semiconductor materials like Silicon Carbide (SiC) have become the mainstream choice for high-end PCS, further enhancing power density and efficiency.
- High Conversion Efficiency Design: Chasing Every “Percentage Point”
The efficiency of the PCS directly impacts the final profitability of the energy storage system. Key strategies for improving efficiency include:- Adopting advanced power devices: Such as SiC-MOSFETs and GaN (Gallium Nitride) devices, which offer inherent advantages like fast switching speed and low conduction loss.
- Optimizing control algorithms: Employing techniques like Model Predictive Control (MPC) to reduce unnecessary switching actions.
- Enhancing thermal management: Using efficient cooling technologies like liquid cooling to ensure components operate within their optimal temperature range.
- Wide DC Voltage Adaptation Range: Strong “Compatibility”
Battery packs of different capacities and brands have vastly different DC voltage ranges. An excellent PCS must have a wide DC voltage input range (e.g., 300V to 1500V) to flexibly adapt to various battery technologies, ensuring stable and efficient operation throughout the entire battery charge/discharge cycle. - Fault Protection and Grid Adaptability: The Reliable “Security Guard”
The PCS integrates multiple comprehensive protection mechanisms:- Electrical protection: Over/under voltage, overcurrent, short circuit, and reverse connection protection.
- System protection: Overtemperature protection, and islanding detection and protection (to prevent dangerous self-supply during grid outages).
- Grid-friendly operation: Must possess the aforementioned fault ride-through capabilities like LVRT/FRT, which are mandatory requirements for grid connection.
- Grid-Connected & Off-Grid Dual-Mode Operation: The Seamlessly Switching “Dual-Mode Expert”
Advanced PCS support flexible switching between two operational modes:- Grid-Tied Mode: Connected to the main grid, participating in energy dispatch.
- Off-Grid or VFI Mode: In Voltage and Frequency Independent (VFI) mode during a grid outage, the PCS can quickly disconnect from the main grid and independently establish a stable local microgrid to supply critical loads. This function is crucial for backup power in emergencies and for powering remote areas.
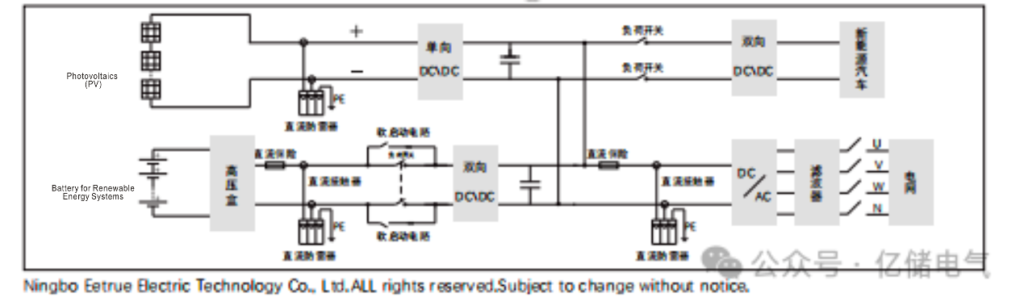
4. Typical PCS System Composition
A complete energy storage PCS system typically consists of:
- AC Side Unit: The grid connection interface, including circuit breakers, AC filters, and an optional transformer.
- DC Side Unit: The battery interface, including DC fuses/circuit breakers, a pre-charge circuit, and DC contactors.
- Power Conversion Unit: The core of the PCS itself—the power module—which performs the AC/DC conversion.
- Control and Communication Unit: The system’s “nerve center,” responsible for running control algorithms, monitoring status, and facilitating real-time communication with the Battery Management System (BMS) and Energy Management System (EMS).
5. Typical Applications, Core Functions, and Value of Energy Storage PCS
Large-scale Energy Storage Power Stations: Smoothes the output of solar energy power plants, participates in grid peak shaving and frequency regulation, and enhances renewable energy integration capacity.
Commercial & Industrial Energy Storage: Enables arbitrage using time-of-use (TOU) rate differentials, reduces demand charges, and serves as backup power to improve supply reliability.
Microgrid/Off-grid Systems: Provides self-sufficient energy systems for islands, mountainous areas, and other remote locations, allowing for coordinated optimization with diesel generators.
Grid Ancillary Services: Delivers advanced services such as frequency regulation, operating reserve, and black start, improving power system flexibility and resilience.
Residential Energy Storage: Facilitates household energy self-management, increases the self-consumption rate of photovoltaic power, and ensures an uninterrupted supply for critical loads.
6.Conclusion
As an indispensable core component within energy storage systems, the technical performance of the Power Conversion System (PCS) directly determines the overall system’s conversion efficiency, operational reliability, and grid support capabilities. With continuous advancements in power electronics, digital control technology, and artificial intelligence algorithms, future PCS technology will evolve towards higher efficiency, greater power density, enhanced intelligence, and increased modularity, providing crucial technological support for realizing a clean, low-carbon, safe, and efficient modern energy system.
7. CNCOB PCS Product Advantages
7.1 Stability
- Incorporates a third-generation DSP+FPGA dual-core architecture, significantly improving operating frequency and instruction execution speed.
- Employs a Hybrid Multi-Decoupling HCMD Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) algorithm to accurately extract the voltage and frequency of the grid’s fundamental component. This enables a timely response to grid voltage disturbances, enhancing grid-connected stability and robustness.
- Features a layered structural design that separates heat sources from the control system, improving thermal dissipation, lifespan, and stability, with an IP65 rating for dust and water resistance.
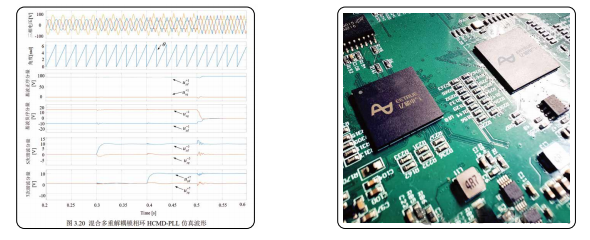
7.2 Safety
- Utilizes optical fiber drive technology, replacing electrical signals with optical signals. This provides high-voltage optical and electrical isolation for control and drive signals, resulting in a more stable and secure control system.
- Offers efficient thermal management with optional intelligent air-cooling or liquid cooling systems. The intelligent air-cooling employs heat pipe and refrigerant technology, while the liquid cooling system features a proprietary flow channel design for efficient heat transfer. This enhances the heat dissipation efficiency of power devices, ensuring full power output and protecting revenue potential.
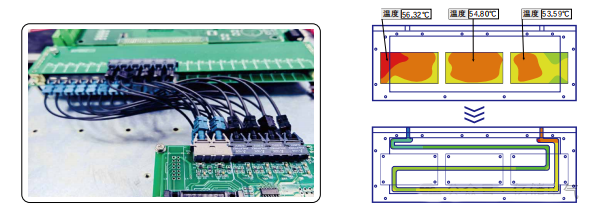
7.3 Scalability
- Supports scalable multi-level operation modes. Appropriate DC/DC and PCS modules can be configured per the application scenario to ensure the reliable operation of multi-source (DC and AC) common DC bus energy storage systems.
- Provides scalability for high/low voltage and power levels. Its modular functional design allows rapid response to customized requirements across different voltage and power ratings. It supports parallel operation modes and features expandable communication and control interfaces compatible with third-party external Energy Management Systems (EMS).
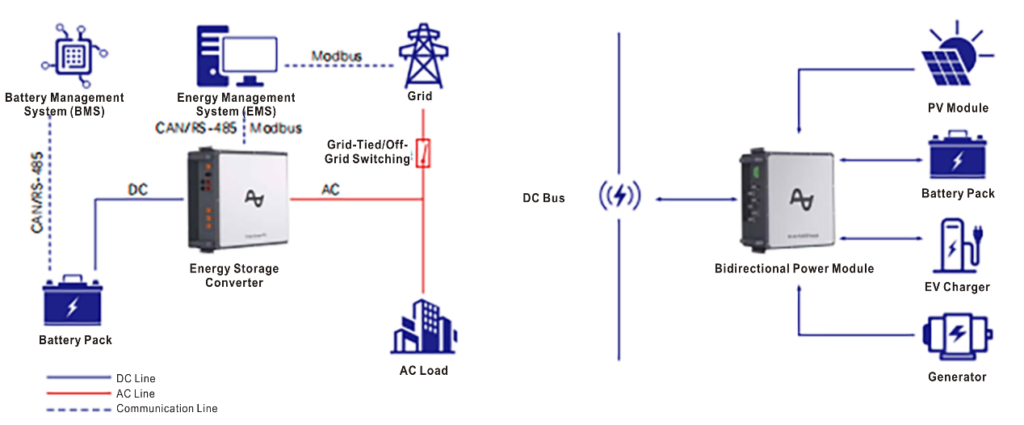
7.4 Ease of Maintenance
- Employs a modular system architecture with independently assembled core modules, allowing for minute-level disassembly and repair by end-users. This design is ideal for commercial and industrial storage/charging operation and maintenance scenarios, ensuring low maintenance costs. Component selection prioritizes durability and lifespan, avoiding low-cost options in favor of high-performance, long-life components such as IGBT modules, film capacitors, and laminated busbars.
- Enables cloud-based fault data sharing, with technical support available online 12 hours a day, 7 days a week.


7.5 EETRUE 60kW-300kW Bidirectional DC/DC Power Converter – Product Features

- Flexible Configuration: Offers expandable multi-level modes and supports a common DC bus structure.
- High-Power Bidirectional Flow: Facilitates bidirectional energy flow on a 1000V high-voltage DC bus. The DC input side supports a constant current mode with a maximum current of 300A.
- Efficient Thermal Management: Utilizes a heat pipe and layered design for optimal cooling.
- Wide Voltage Compatibility: Features a broad input/output DC voltage range, compatible with systems from 200Vdc to 1000Vdc.
- Broad Integration: Compatible with new energy storage batteries, photovoltaic modules, and new energy vehicle integration.
- Configurable Functionality: Can be configured with functional modules for Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G), Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT), and mobile power station smart charging robot DC fast charging.
- Modular Design: Ensures more convenient maintenance.