Exploring the Various Applications of Coal
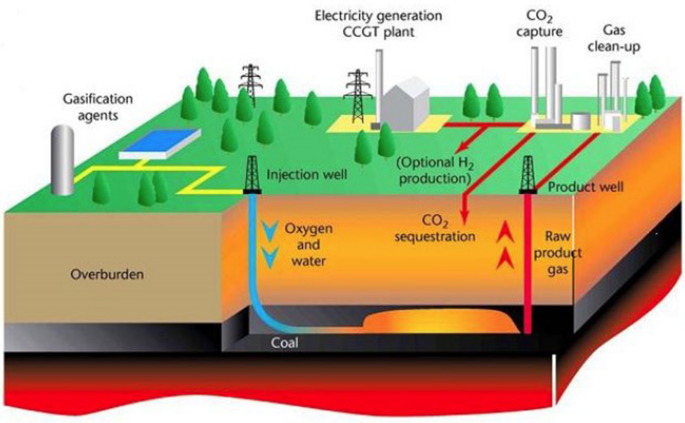
Coal has been a foundational resource fuelling the development of human civilisation for centuries. Its versatility has seen it applied in a plethora of ways, some of which continue to be relevant in modern times. Despite the growing emphasis on sustainable and renewable energy sources, coal remains a vital component in various industries, and its utility extends beyond just energy production. Let’s delve into the diverse applications of coal and understand how its different forms are utilised in today’s world.
The Role of Coal in Energy Generation
At the fundamental level, coal is predominantly used as a fuel for electricity generation. Power plants convert the thermal energy from burning coal into electrical energy, which is then distributed across power grids. The heat produced by combustion boils water, creating steam that drives turbines, which in turn activate generators to produce electricity. This reliable source of energy supports the electricity needs of millions globally.
Industrial Uses of Coal
In various industries, coal acts as a reducing agent in the production of metals from their ores, especially in the iron and steel industry. Coking coal, a high-carbon form of coal, is essential in blast furnaces for manufacturing steel—an integral material for construction, transportation, and manufacturing sectors. Moreover, coal is used to produce coke, which is a porous, hard black rock of concentrated carbon that is essential for metallurgical processes.
The Importance of Anthracite Coal
Anthracite coal, a high-grade coal with a high carbon content and low sulphur levels, is revered for its purity and energy density. It is a premium coal product used both domestically and industrially as it burns cleaner than other forms of coal and produces more heat. Thus, anthracite coal is greatly sought after for applications such as home heating and water filtration.
Coal in the Manufacturing of Cement and Paper
Coal finds its use in the production of cement—the key ingredient in concrete. The combustion of coal produces high temperatures necessary to create clinker, which is then ground into fine powder to make cement. Furthermore, coal by-products are utilised in the paper industry, where they serve as a component for paper manufacturers to produce high-quality paper. The industrial uses of coal cannot be understated, as it plays an integral role in many manufacturing processes.
Coal Dust and its Applications
One might be surprised at the utility of coal dust, a fine powdered form of coal. It has specific uses in industrial settings, including serving as a filter media. Due to its adsorbent properties, coal dust can be employed in water treatment facilities to remove impurities, ensuring cleaner, safer water. It is also used in the manufacturing of construction materials like bricks, tapping into the binding properties of coal dust to enhance structural integrity.
The Technological Edge in Coal Processing
As technology advances, processing coal has become more efficient, leading to better quality products with higher carbon content and fewer impurities. This not only optimises the performance of coal-based products but also helps to address environmental concerns associated with coal handling and use. Innovative companies focus on the development of processes that yield superior coal products while minimising the environmental footprint.
Environmental Technologies and Coal
The coal industry is acutely aware of the ecological impact of coal mining and combustion. As a result, efforts are continuously made to implement cleaner coal technologies. These technologies aim to reduce emissions of pollutants such as sulphur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter. Approaches such as flue gas desulphurisation and advanced coal combustion methods help in achieving more environmentally-sound practices.
Coal in Domestic Heating
Despite the advent of modern heating systems, coal remains a primary source of heating in several countries. The high heat output and long burn time of anthracite and bituminous coal make them suitable for heating homes during colder seasons, especially in areas where coal is abundant and affordable.
Contribution to the Chemical Industry
Coal derivatives, such as coal tar and coal gas, play a vital role in the chemical industry. Coal tar is used in manufacturing pharmaceuticals, synthetic dyes, and plastics. Meanwhile, coal gas, a by-product of coal distillation, serves as a fuel in some industrial operations and as a feedstock for the production of synthetic natural gas.
The Economic Aspect of Coal
Coal continues to be an economic boon for many countries, providing employment opportunities and contributing to national revenues. Mining, transportation, and processing of coal support local economies and are a significant consideration in national energy policies. The coal industry’s economic impact cannot be dismissed despite the global shift towards greener energy sources.
James Cumming & Sons
A leading example in the coal industry is James Cumming & Sons. Established in 1909, they have demonstrated a commitment to quality and environmental responsibility in all their products and practices. Their expertise in the field illustrates the potential of coal to be utilised responsibly while meeting the needs of diverse industries.
Coal in Filtration Systems
Expanding beyond energy and industrial use, coal is instrumental in filtration systems. Specific grades of coal, when processed into activated carbon, have a vast surface area that traps contaminants. These characteristics make coal-based activated carbon a favoured choice in both water and air filtration systems.
Looking to the Future
While coal has its challenges, particularly in terms of environmental impact, innovation and responsible management can harness its potential in a way that balances industrial needs and ecological considerations. Advancements in coal utilisation and processing continue to redefine its role in a modern, sustainable society.
Conclusion
Coal’s importance spans countless applications across different industries. From energy production to water treatment, metallurgy to domestic heating, and even chemical manufacturing, the various forms of coal, including anthracite coal and coal dust, play a pivotal role. Businesses like James Cumming & Sons are at the forefront of innovation, ensuring that coal continues to be a viable and valuable resource. Coal’s multifaceted applications showcase why it remains a cornerstone of global industry and economy, even as the world progresses towards greener and cleaner energy alternatives.




